Holter Monitors in Cardiac Care
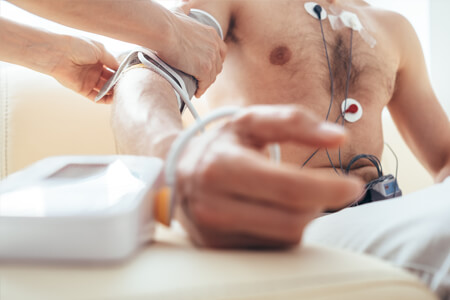
The role of diagnostic tools in providing precise, timely, and accurate cardiac care assessments cannot be overstated. Among the array of diagnostic devices available, the Holter monitor stands out as a crucial instrument in the management of various cardiac conditions.
Understanding the importance of Holter monitors is essential not only for healthcare professionals but also for patients seeking optimal cardiac care and health.
The Significance of Holter Monitors
Holter monitors, named after Dr Norman J. Holter who pioneered ambulatory electrocardiography, are portable devices designed to continuously record the electrical activity of the heart over an extended period, typically 24 to 48 hours, or even longer in some cases. Unlike standard electrocardiograms (ECGs) performed in clinical settings, which provide only a snapshot of the heart's activity, Holter monitors offer a more comprehensive evaluation by capturing data during the patient's daily activities, including sleep and exercise.
Conditions Diagnosed with Holter Monitors
Holter monitors play a pivotal role in diagnosing various cardiac arrhythmias, which are abnormalities in the heart's rhythm.
Some of the conditions detected by Holter monitoring include:
1. Atrial Fibrillation (AF): AF is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia, characterised by rapid and irregular electrical impulses in the atria, leading to inefficient blood pumping. Holter monitors aid in detecting intermittent episodes of AF that may not be captured during routine ECGs, enabling timely intervention to prevent complications such as stroke and heart failure.
2. Ventricular Arrhythmias: These abnormal heart rhythms originate in the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart. Ventricular arrhythmias, including ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, can be life-threatening if left undiagnosed and untreated. Holter monitoring helps identify such arrhythmias, guiding physicians in formulating appropriate management strategies.
3. Bradycardia and Tachycardia: Holter monitors are instrumental in identifying episodes of bradycardia (abnormally slow heart rate) and tachycardia (abnormally fast heart rate), which may occur intermittently and remain asymptomatic. Early detection allows clinicians to assess the underlying causes and initiate targeted interventions.
4. Syncope Evaluation: Syncope, commonly known as fainting, can result from various cardiac and non-cardiac causes. Holter monitoring aids in capturing cardiac arrhythmias associated with syncope, facilitating accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans to prevent recurrences.
Role of Holter Monitors in Cardiac Care Treatment
The data obtained from Holter monitoring serves as a cornerstone in managing cardiac arrhythmias. Based on the findings, healthcare providers can formulate individualised treatment strategies aimed at optimising patient outcomes.
Treatment modalities may include:
1. Medications: For certain arrhythmias, such as AF, medications like antiarrhythmic drugs or anticoagulants may be prescribed to control heart rhythm and prevent complications like stroke.
2. Cardioversion: In cases of persistent AF or other sustained arrhythmias, electrical cardioversion may be performed to restore normal heart rhythm.
3. Catheter Ablation: For patients with recurrent or drug-refractory arrhythmias, catheter ablation, a minimally invasive procedure, may be recommended to destroy abnormal heart tissue responsible for generating arrhythmias.
4. Device Therapy: In some instances, implantable devices such as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) may be indicated to regulate heart rhythm and deliver appropriate therapies in response to detected arrhythmias.
Why Doctors Refer Patients for Holter Monitoring
Physicians may refer patients for Holter monitoring based on various clinical indications, including:
1. Symptoms of Palpitations: Patients experiencing palpitations, irregular heartbeats, dizziness, or unexplained fainting episodes may undergo Holter monitoring to assess for underlying arrhythmias.
2. Evaluation of Antiarrhythmic Therapy: Patients receiving antiarrhythmic medications may require periodic Holter monitoring to assess treatment efficacy, detect drug-induced arrhythmias, and adjust medication dosages accordingly.
3. Post-Cardiac Interventions: Following cardiac procedures such as catheter ablation or device implantation, Holter monitoring helps evaluate procedural success, detect recurrence of arrhythmias, and monitor device function.
4. Risk Stratification: Individuals with risk factors for cardiac arrhythmias, such as hypertension, diabetes, or a family history of sudden cardiac death, may undergo Holter monitoring as part of risk stratification and preventive cardiac care.
Essential Testing Information
Before undergoing Holter monitoring, patients should be adequately informed about the procedure and instructed on proper device usage.
Key aspects of Holter monitoring include:
1. Preparation: Patients are typically advised to maintain their usual daily activities during the monitoring period while avoiding activities that may interfere with the device or electrode placement.
2. Electrode Placement: Electrodes or small patches are securely attached to the patient's chest, connected to the Holter monitor device worn on the body, usually clipped to a belt or carried in a pouch.
3. Diary Documentation: Patients may be instructed to keep a diary documenting their activities, symptoms, and any notable events during the monitoring period, providing valuable context for interpreting the recorded data.
4. Return and Analysis: After the monitoring period, patients return the device to the healthcare facility, where the recorded data is analysed by specialised technicians or cardiologists to identify arrhythmic events and correlate them with clinical symptoms.
Holter monitors play a vital role in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of various cardiac arrhythmias, providing valuable insights into the heart's electrical activity over an extended period.
At SmartCare Diagnostics in Brisbane, Australia, the integration of Holter monitoring into cardiac care services underscores a commitment to delivering comprehensive and patient-centred care.
By understanding the significance of Holter monitors, patients and healthcare professionals alike can collaborate effectively to promote optimal cardiac health and well-being.
Why wait or pay too much for diagnostic tests?